A Primer on Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM)
While other modulation schemes discussed in this blog series (pulse, frequency, amplitude, phase) date back to the early chapters of RF engineering history, quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) was first described by C. R. Cahn in 19602 and evolved steadily over the next few decades. In the last 25 to 30 years, no modulation scheme has seen such widespread development and application as QAM. The technology has played a pivotal role in the industry’s ability to scale data speed and capacity with user demand by packing more data onto the carrier waveform and pushing a fixed channel bandwidth closer to Shannon’s limit. QAM modulation is used widely in cellular networks and backhaul, CATV networks and fixed wireless access points (802.11), and satellite communications to name a few. See Table 3 in Reference [3] for a more detailed list of applications.
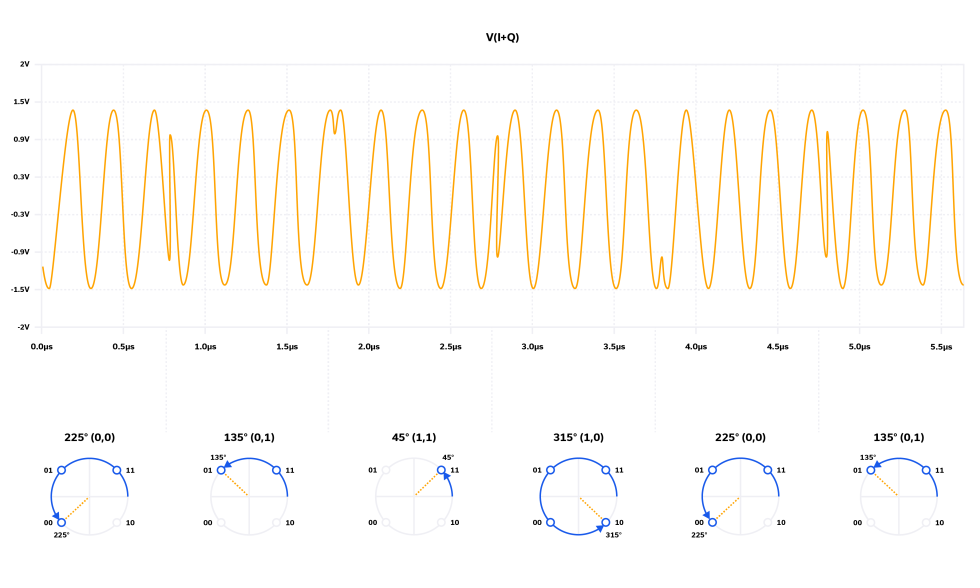
In this article, we describe QAM using basic mathematics and illustrate how a QAM modulator operates. We introduce the concept of a constellation diagram and how it relates to the time domain plots for QAM modulation. A representative set of components is then utilized to design a functional QAM modulator by way of illustration. We conclude by describing how the QAM signal is demodulated at the receiver.
A Quick Guide to Mixer Topologies
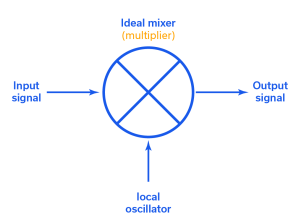
Real-world mixers come in many flavors. Mini-Circuits offers hundreds of unique mixer models representing six different circuit topologies. The good news is that this variety gives designers options for just about every application requirement. The problem, albeit a high-class problem, is that understanding the differences between mixer designs can complicate the component selection process.
This article will provide a broad overview of the different mixer topologies, including both balanced and unbalanced architectures. It should be noted that, in theory, any nonlinear device can be used to make a mixer, but Schottky diodes and Field Effect Transistors (FETs) are the most common. Mini-Circuits designs both diode- and FET-based mixers, but the topologies here will be presented using diode mixers for simplicity. However, the same principles can be applied to other technologies as well.




