RF/Microwave Bias Tees from Theory to Practice
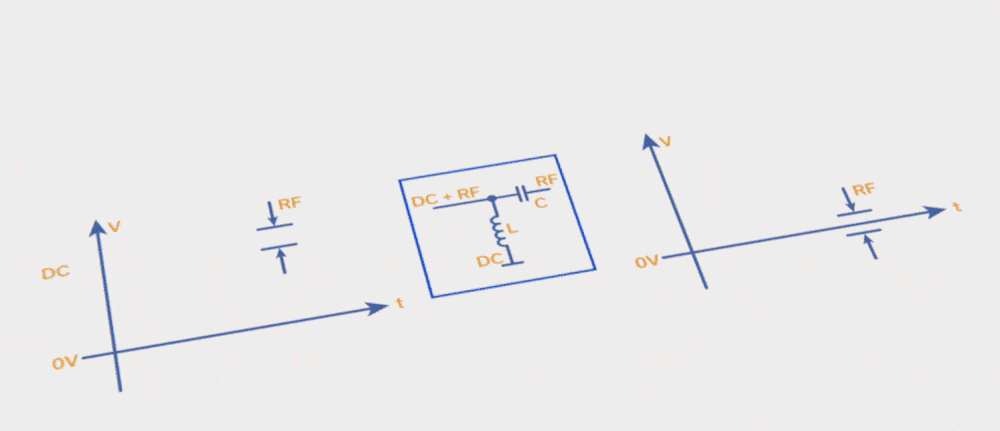
The bias tee is an essential component for applying DC voltage to any component that must also pass RF/microwave signals, most commonly an RF amplifier that requires a DC supply. For narrowband applications, bias tee design and construction are relatively straightforward, provided attention is paid to component self-resonant frequencies (SRFs). For broadband applications, however, bias tee design and construction are nontrivial, and attention to component characteristics is paramount to a successful, high-performance design. In this article, we examine narrowband bias tee design, component SRFs, and how they impact the design, then extend those ideas to broadband bias tees. We will also compare the electrical and physical performance attributes of different types of broadband bias tee designs including discrete circuits with conical inductors as well as MMICs.
BOOST YOUR KNOWLEDGE: A COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO RF BIAS TEES – TYPES AND APPLICATIONS EXPLAINED

RF Bias Tees are electronic devices that are used to combine DC power and RF signals on a single transmission line. These devices are used in a wide range of applications, including wireless communication systems, test and measurement equipment, and RF circuit design. RF bias tees can also be used to power active RF components, such as amplifiers and mixers, while also allowing the RF signal to pass through the device.
ביטול השימוש ב-Bias Tee במוצא של מגברי Push–Pull באמצעות שימוש בשנאי 3:1 לא מאוזן למאוזן TCM3–452X+
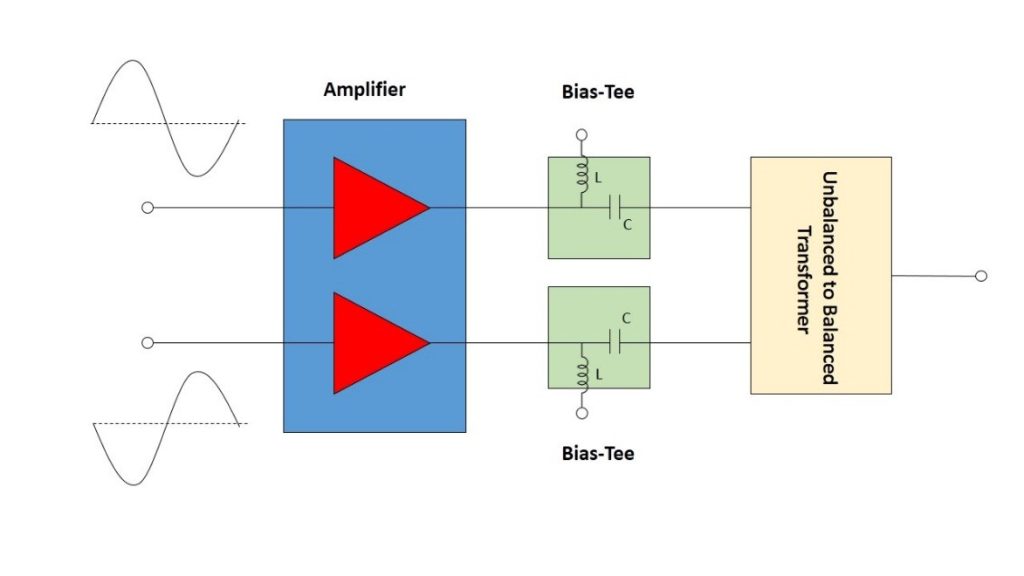
מגברי Push-Pull (דחף-סחב) משמשים במערכות מרובות אוקטבות כדי לשפר את הספק המוצא והנצילות של המגבר, לדכא הרמוניות לא רצויות ולשפר את הטווח הדינמי של המערכת. בתכנון של מגבר Push-Pull אות המקור מסופק לשני טרנזיסטורים או מגברים מתואמים במקביל וביחס מופע (פאזה) של 180º. כאשר מחברים אותם מחדש בעזרת התקן מסכם שני בהזזת מופע של 180º, האותות הבסיסיים נמצאים במופע אחד ובסיכום של פעמיים ההספק של כל מחצית, שעה שההרמוניות מסדר זוגי הן במופע הפוך, וכך מתבטלים באופן אידיאלי האותות הבלתי רצויים האלו. במציאות, חוסר האיזון של המופע והמשרעת (אמפליטודה) של מעגלי הפיצול והסיכום גורם ל”קלקול” של הביטול האידיאלי. עם זאת, התוצאה הנקייה היא עדיין דיכוי משמעותי של ההרמוניות הזוגיות, בדרך כלל ב- 20 dB עד 40 dB.
Eliminating Bias Tees from Push-Pull Amplifier Outputs Using TCM3-452X+ 3:1 Unbalanced-to-Balanced Transformer
Push-pull amplifiers are used in many multi-octave systems to enhance amplifier output power and efficiency, suppress unwanted harmonics and improve system dynamic range. In a push-pull amplifier design, two matched transistors or amplifiers are supplied by the source signal in parallel and at a 180° phase relationship. When re-combined through a second 180° phase shifting combiner, the fundamental signals are in-phase and combined at twice the power of each half, while the even order harmonics are out-of-phase, creating ideal cancellation of these unwanted signals. In reality, the phase and amplitude unbalance of the splitting-combining circuits result in degradation of the ideal cancellation. However, the net result is still significant suppression of the even harmonics, typically by 20 to 40 dB.





