Phase-Matched Cable Assemblies
Phase-matched cable assemblies are ubiquitous, and modern-day phase matching requirements serve to drive their growing popularity. As electrical length matching requirements have tightened to less than one or two degrees, the mechanical precision with which various styles of cable are constructed has improved to keep pace. Additionally, dielectrics more exotic than tried-and-true Teflon are being researched and introduced to afford greater phase stability. Volumes have been written on how to phase-match cable assemblies and dozens and dozens of companies practice this discipline. Why is phase-matching so prevalent, and why does it matter so much? In this article we answer these questions by highlighting many phase-matched cable applications and the effect of varying phase length on systems in the RF/microwave domain. We also describe Mini-Circuits’ capabilities in the phase-matching cable arena.
Phase Matching Near and Far: DC-to-UV
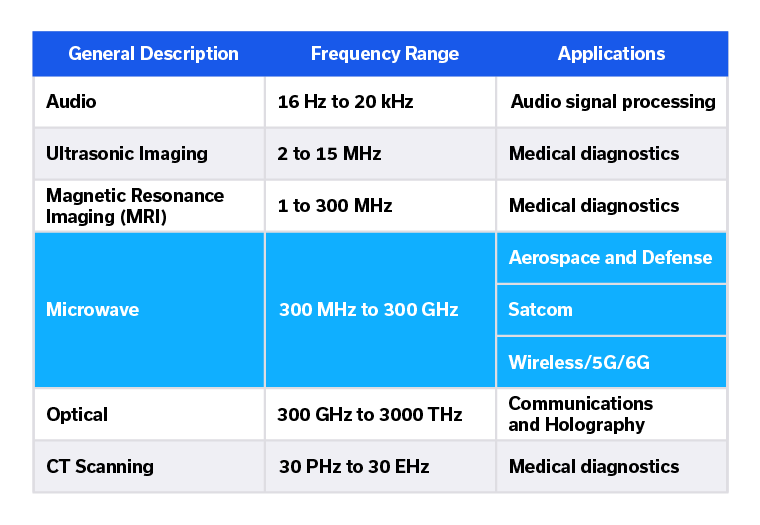
Phase matching is utilized from the lowest of low audio frequencies (16 Hz)1 through microwave and visible light and into the ultraviolet spectrum2. Phase-matched cables are common because they are utilized in so many disciplines and frequency ranges. Consider the span of frequencies shown for the phase-matched cable applications of Table 1. The number of applications in the microwave spectrum alone is endless, in large part due to the fact that phase-matched cables are an essential ingredient in virtually all phased array systems.4 In addition to microwave, even ultrasonic and magnetic resonance imaging systems include phased array concepts and phased array optics are becoming increasingly popular.
The Importance of Phase Matching
Use Case 1: Phase-Matched Cables in Phased Array Antennas
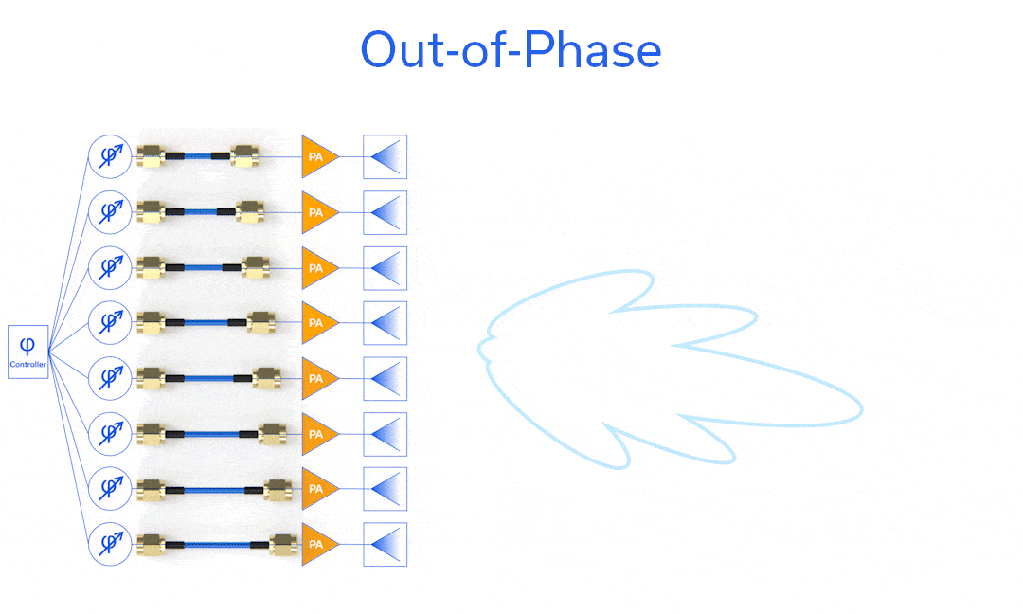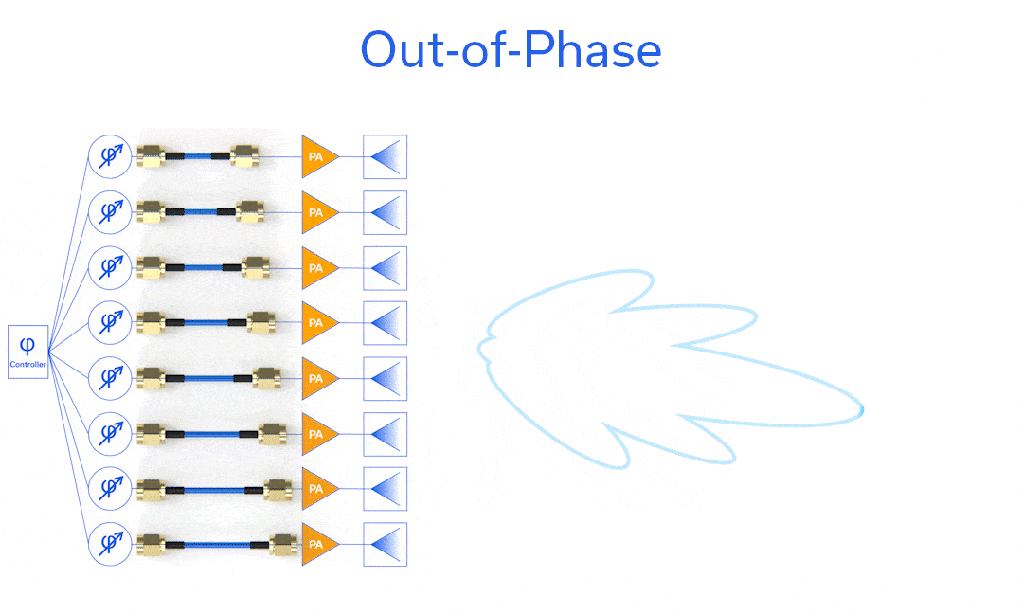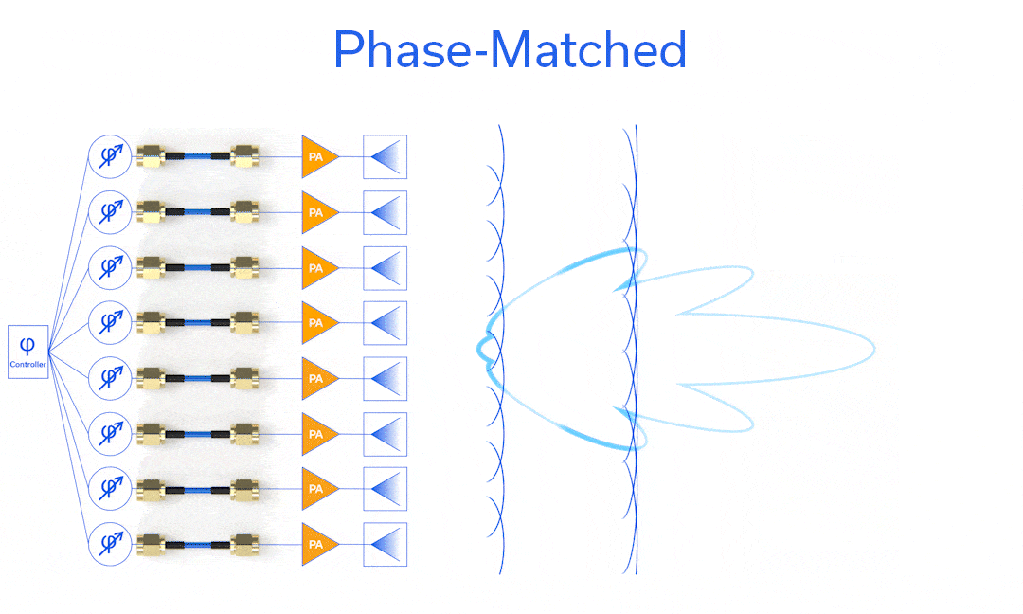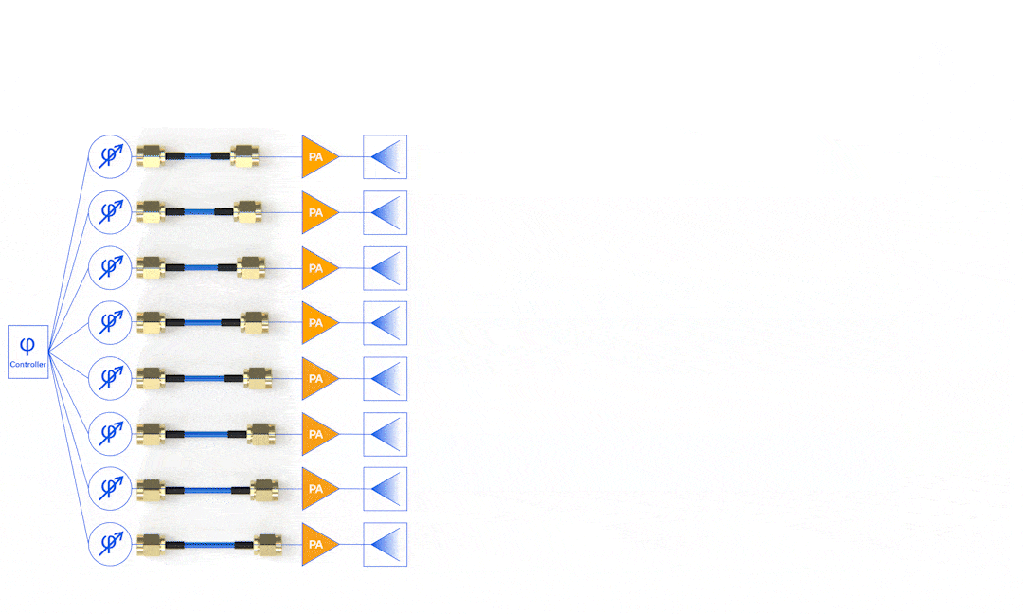
Phase matching is critical in certain applications, and perhaps no application demands tighter phase control than the phased array. The phase of each of the n elements has an impact on the shape and direction of the radio frequency beam, since all n elements are superimposed. Each element or group of elements has a variable phase shifter to steer the beam, but controlling the calibration of these phase shifters would be quite cumbersome if the array were plumbed with cables of significantly different electrical lengths. Shown in Figure 1 is a demonstration of what would happen if nonuniform phase length cables were utilized to feed the phased array shown. Note in (a) that with phase-matched cables the main lobe and sidelobes are symmetric about the antenna centerline (x-axis, boresight) but in (b) cables of varying phase lengths cause the radiation pattern of the main lobe and sidelobes to shift slightly in the -y direction.
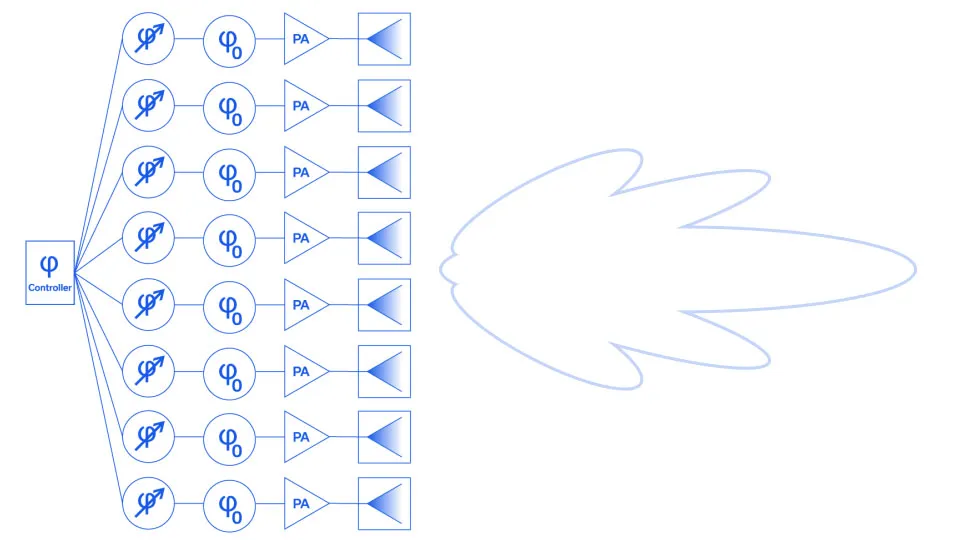
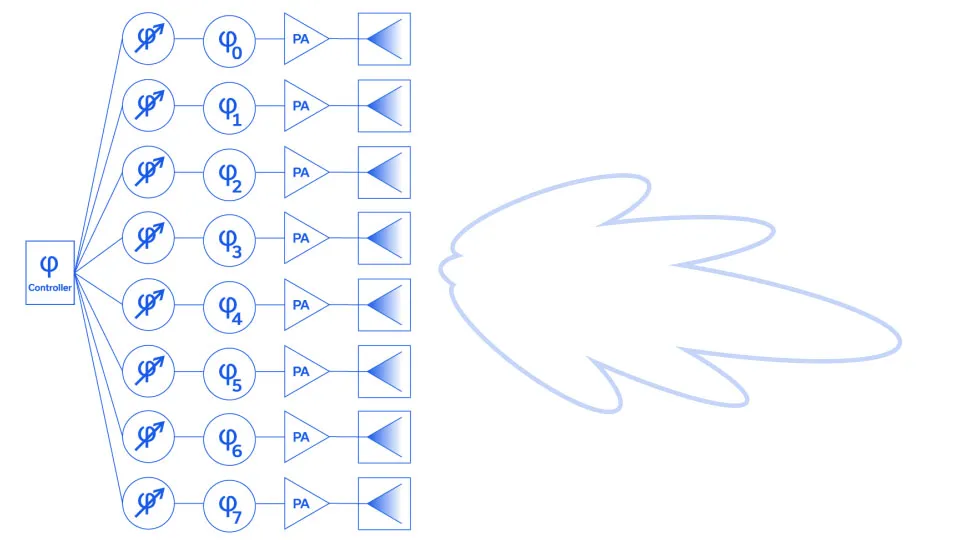
Figure 1: Beam formed by notional phased array system (a) with phase-matched cables (φ0) feeding the elements and (b) with cables of various phase lengths (φ0 through φ7) feeding the phased array elements.
Consequently, cables utilized to build phased arrays for radar, EW, 5G, 6G, WLAN, and Satcom systems will generally come with tight unit-to-unit (relative) and perhaps even tight absolute phase length requirements, often on the order of ± 1⁰. While ± 1⁰ in length for an old-school C-band radar is no big deal, for a 5G NR FR2 beamformer approaching mmWave, the dimensional tolerances that must be maintained are extremely small. Some cable-to-cable variation in phase can be taken up by the in-line phase shifter for each element or group of elements in an array, but not so much as to limit the azimuth or elevation of the scanning range, or that it overcomplicates the calibration process. After all, cables sometimes need to be replaced, and complicated calibration processes can be expensive to perform.
Use Case 2: Phase-Matched Cables in Test & Measurement
Systems operating with internal, multi-channel phase matching most often require phase matching externally to transport signals to test and measurement equipment. These external, phase-matched test cables come in a variety of sizes, with a multitude of connectors, and varying degrees of precision. Systems with multiple antenna elements, such as phased arrays, often require a large set of phase-matched cables with which to perform over-the-air testing. Additionally, modern multiple-transceiver communications systems have tight synchronization and phase-coherence requirements, thereby necessitating a set of phase-matched cables to perform system test. In the semiconductor testing realm, wafer probing of multi-channel, phase-coherent MMICs requires very tight phase matching from the probe back to the test and measurement equipment. In addition to being required externally (between the system being tested and the test and measurement equipment), phase-matched cables are also required to maintain precision phase relationships internal to test and measurement equipment itself, such as inside a vector network analyzer (VNA) and a spectrum analyzer.
Mini-Circuits’ Phase-Matched Cable Solutions
Shown in Table 2 are the cable types most often specified to be phase-matched. The FL086-series, as the name implies, is an 0.086” center diameter, hand-formable cable with a flexible interconnect system that allows a different frequency range to be achieved for each connector selection. The 141-series has a robust 0.141” center diameter and is also hand-formable. This series also comes replete with a flexible interconnect system that includes supporting N-type connectors.
| Series | Frequency (GHz) | Connector Style | Part Number (12-Inch) |
| FL086- | 6 | SMA/MCX | FL086-12SMMCR+ |
| 18 | SMA | FL086-12SM+ | |
| 26.5 | 3.5 mm | FL086-12-35M+ | |
| 40 | 2.92 mm | FL086-12KM+ | |
| 141- | 12.5 | SMA/N | 141-12SMNB+ |
| 18 | SMA | 141-12SM+ | |
| ULC- | 18 | SMA | ULC-1FT-SMSM+ |
Table 2: Cable types most commonly specified to Mini-Circuits for use in phase-matched applications.
The ULC-series of flexible test cables are rugged and reliable and are often specified as phase-matched sets and utilized to test a variety of multi-antenna element or multi-channel systems. Mini-Circuits has designed many more cable types to exacting, custom phase matching specifications, and all of these are available upon request. Should the need for special phase-matched cables arise, rest assured Mini-Circuits has experience in that lane and can meet your requirements.
The Final Phase
Phase-matching cables is currently so prevalent that requirements are found literally from DC to UV. Phase matching is even more commonplace than the phased array antenna itself, because testing phased array systems often requires phase-matched cables. Any errors in the electrical length of the phase-matched cables for beamforming can result in distortion of the main beam and skewing of its direction as shown in Figure 1. Ensuring that the phase length of the test cables feeding a phased array antenna match one another within a very close tolerance is one challenge for test and measurement system engineers. Characterizing multi-channel, phase-coherent systems is another challenge in the test and measurement environment, where accurately matched test cables are required to maintain precision phase relationships. Mini-Circuits has excellent capabilities in the phase-matching cable arena, and we continue to design and build custom solutions for our customer base. Whether you need cables for an airborne system or your laboratory-based test setup, look to Mini-Circuits for a standard or custom solution.
References
- What is Phase Matching Bass and should I use it? | AVS Forum
- Section 1: Laser Fundamentals (princeton.edu)
- More than Just a Phase: Understanding Phase Stability in RF Test Cables – Mini-Circuits Blog (minicircuits.com)
- A Brief Overview of Phased Array Systems – Mini-Circuits Blog (minicircuits.com)
- RF Cables – 2.4mm, 2.92mm, SMA, N-Type, F-Type, BNC, RF Test Cables | Mini-Circuits